Heating Systems: Which one should you choose?

With the UK government recently announcing new grants encouraging people to install heat pumps into their homes alongside ever increasing energy costs many people have been considering which heating system is the right one for them, and whether it is possible to switch to a greener, cheaper system.
So which type of heating system should you choose?

Gas Boilers
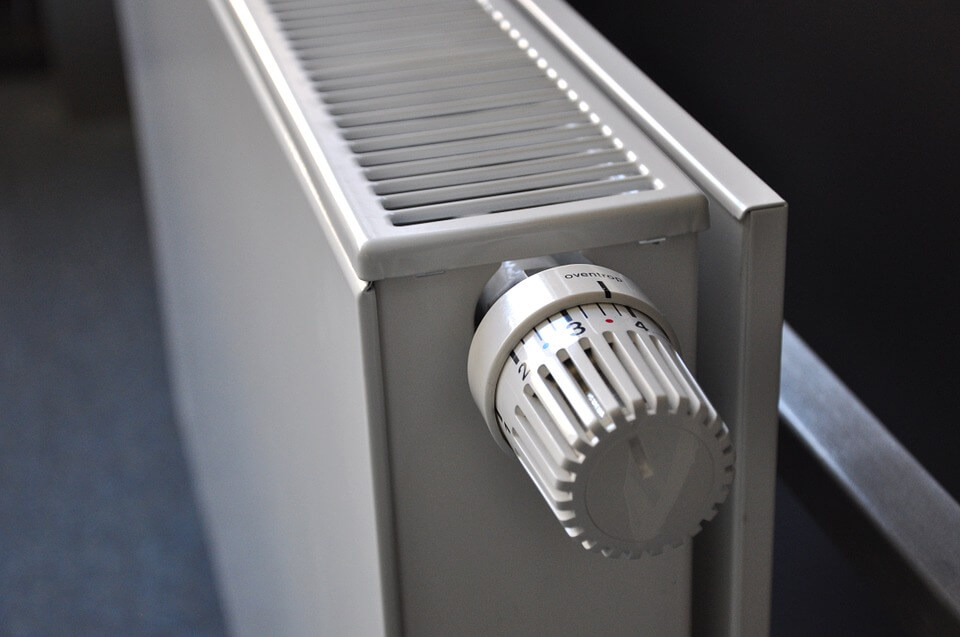
In 2021, it was found that 77% of UK residents heat their home using a gas central heating system. However, gas heating currently contributes to 21% of the UK’s carbon emissions which people are keen to reduce.
Gas central heating systems work by heating water in pipes over gas flames within the boiler. This water then travels around the pipes in the house into radiators which then heat the room through convection. The system is usually controlled by a thermostat that will be set to switch the heating on when the house falls below a set temperature.
The main benefit of a gas central heating system is that is cheaper to run compared with an electric system, and can meet the high demand for hot water and heating in bigger homes. There are also a much greater range of gas boilers on the market, and are a much more affordable option for houses already connected to the gas network.
However, despite gas central heating systems being the most popular heating system in the UK, people are now having to think of alternative systems since the release of the Government’s Heat and Building Strategy in October 2021. The strategy aims to move away from fossil fuel heating systems such as gas central heating and by 2035 intends for all new systems installed into UK homes to be low carbon technologies. However, this does not mean that you have to get rid of your existing gas central heating system it just means any new system cannot be fuelled by gas after this date.

Electric Boilers
Electric boilers are a low carbon option that not many people are talking about. Electric boilers work in a similar way to gas boilers, only the water is heated by an element, like in your kettle. They draw energy from the national grid so most houses are able to have an electric boiler installed. They are also easier to install than gas boilers as there is no need for a flue pipe.
Electric boilers do not come with the same risks as gas boilers such a carbon monoxide leaks if the boiler is faulty and they also have few moving parts so there is less chance of something malfunctioning. Electric boilers can also be better for the environment as they draw their energy from electricity and not burning natural gas. The UK is moving away from producing electricity through burning fossil fuels and moving to more renewable sources such as wind and solar power. Therefore, the energy used will be low carbon compared to burning natural gas. The electric boiler is also up to 100% efficient, compared with the 95% efficiency of gas boilers.
The biggest downside to electric boilers though is the cost. Firstly, as there are many more gas boilers on the market to choose form you are more likely to find a cheaper gas boiler than electric. Secondly, the cost of running an electric boiler is significantly higher than gas as pence per kWh of electricity is much greater. Electric boilers will also struggle to meet the high demand of big houses and would only really be suitable for smaller houses and flats.

Hydrogen Boilers
Hydrogen boilers are another low carbon alternative that could replace gas boilers in the near future. They are not currently for sale, however, multiple companies are working on prototypes with a hope to start marketing them soon.
Hydrogen boilers work very much the same way as gas boilers, however, instead of burning natural gas, the boiler burns hydrogen and uses the energy released to heat the water in the system. The by-product of this reaction is water which can be condensed and removed from the boiler.
This system very much relies on the availability of hydrogen gas, which would need to be added to the gas networks already in existence so the boilers could have a supply of hydrogen. This technology is very new, and much more research will be needed before this can be a viable alternative to gas boilers.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are the most recent green technology to win favour with the government, and a whole new grant scheme has been developed to encourage the UK public to get a heat pump installed.
There are different types of heat pump including ground source heat pumps and air source heat pumps. Heat pumps work by absorbing energy from the air or ground and transferring it into a liquid refrigerant. The refrigerant is then compressed to increase the temperature and the heat is transferred to your heating system.
Heat pumps are expensive to install and require a significant amount of space, especially if you are looking into having a ground source pump installed. The Government grant of £5000 will reduce the cost of the installation though, which is worth bearing in mind. Heat pumps also reduce carbon emissions as no fossil fuels are burnt in the production of the heat energy.
🆕 £5k grants for heat pumps & other low carbon heating.
By 2030 heat pumps should cost the same as gas boilers.
Reducing our dependency on fossil fuels & exposure to global price spikes.
Full Heat & Buildings Strategy
👉 https://t.co/8qmT5FjXMN#TogetherForOurPlanet pic.twitter.com/55bjxcbKvd— Dept for BEIS (@beisgovuk) October 19, 2021
It is also recommended that houses with heat pumps installed have extremely good insulation as heat pumps work at lower temperatures than conventional systems so this is something to consider before having one installed. It is difficult to say whether in the long term a heat pump will be cheaper to run than a gas boiler, however, the government have said they will try to ensure that the cost of running a heat pump is no more than a gas boiler but there is no way to ensure that this will happen.
Back to blog



